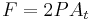Water rocket
A water rocket is a type of model rocket using water as its reaction mass. The pressure vessel—the engine of the rocket—is usually a used plastic soft drink bottle. The water is forced out by a pressurized gas, typically compressed air. It is an example of Newton's third law of motion.
The term "aquajet" has been used in parts of Europe in place of the more common "water rocket" and in some places they are also referred to as "bottle rockets" (which can be confusing as this term refers to a firework in other places).
Contents |
Operation
The bottle is partly filled with water and sealed. The bottle is then pressurized with a gas, usually air compressed from a bicycle pump, air compressor, or cylinder up to 125 psi, but sometimes CO2 or nitrogen from a cylinder.
Water and gas are used in combination, with the gas providing a means to store potential energy, as it is compressible, and the water increasing the mass fraction and providing greater force when ejected from the rocket's nozzle. Sometimes additives are combined with the water to enhance performance in different ways. For example: salt can be added to increase the density of the reaction mass resulting in a higher specific impulse. Soap is also sometimes used to create a dense foam in the rocket which lowers the density of the expelled reaction mass but increases the duration of thrust. It is speculated that foam acts as a compressible liquid and enhances the thrust when used with De Laval nozzles.
The seal on the nozzle of the rocket is then released and rapid expulsion of water occurs at high speeds until the propellant has been used up and the air pressure inside the rocket drops to atmospheric pressure. There is a net force created on the rocket in accordance with Newton's third law. The expulsion of the water thus can cause the rocket to leap a considerable distance into the air.
In addition to aerodynamic considerations, altitude and flight duration are dependent upon the volume of water, the initial pressure, the rocket nozzle's size, and the unloaded weight of the rocket. The relationship between these factors is complex and several simulators have been written to explore these and other factors.[1][2][3]
Often the pressure vessel is built from one or more used plastic soft drink bottles, but polycarbonate fluorescent tube covers, plastic pipes, and other light-weight pressure-resistant cylindrical vessels have also been used.
Typically launch pressures vary from 75 to 150 psi (500 to 1000 kPa). The higher the pressure, the larger the stored energy.
Multi-bottle rockets and multi-stage rockets
Multi-bottle rockets are created by joining two or more bottles in any of several different ways; bottles can be connected via their nozzles, by cutting them apart and sliding the sections over each other, or by connecting them opening to bottom, making a chain to increase volume. Increased volume leads to increased weight, but this should be offset by a commensurate increase in the duration of the thrust of the rocket. Multi-bottle rockets can be unreliable, as any failure in sealing the rocket can cause the different sections to separate. To make sure the launch goes well, pressure tests are performed beforehand, as safety is a concern. These are very good if you want to make the rocket go high however they are not very accurate and may veer off course.
Multi-stage rockets are much more complicated. They involve two or more rockets stacked on top of each other, designed to launch while in the air, much like the multi-stage rockets that are used to send payloads into space. Methods to time the launches in correct order and at the right time vary, but the crushing-sleeve method is quite popular.
Sources of gas
Several methods for pressurizing a rocket are used including:
- A standard bicycle/car tire pump, capable of reaching at least 75 psi (520 kPa).
- Water pressure forcing all the air in an empty water hose into the rocket. Pressure is the same as the water main.
- An air compressor, like those used in workshops to power pneumatic equipment and tools. Modifying a high pressure (greater than 15 bar / 1500 kPa / 200 psi) compressor to work as a water rocket power source can be dangerous, as can using high-pressure gases in from cylinders.
- Compressed gases in bottles, like carbon dioxide (CO2), air, and nitrogen gas (N2). Examples include CO2 in paintball cylinders and air in industrial and SCUBA cylinders. Care must be taken with bottled gases: as the compressed gas expands, it cools (see gas laws) and rocket components cool as well. Some materials, such as PVC and ABS, can become brittle and weak when severely cooled. Long air hoses are used to maintain a safe distance, and pressure gauges (known as manometers) and safety valves are typically utilized on launcher installations to avoid over-pressurizing rockets and having them explode before they can be launched. Highly pressurized gases such as those in diving cylinders or vessels from industrial gas suppliers should only be used by trained operators, and the gas should be delivered to the rocket via a regulator device (e.g. a SCUBA first-stage). All compressed gas containers are subject to local, state and national laws in most countries and must be safety tested periodically by a certified test centre.
- Ignition of a mixture of explosive gases above the water in the bottle; the explosion creates the pressure to launch the rocket into the air.[4]
Nozzles
Water rocket nozzles differ from conventional combustion rocket nozzles in that they do not have a divergent section such as in a De Laval nozzle. Because water is essentially incompressible the divergent section does not contribute to efficiency and actually can make performance worse.
There are two main classes of water rocket nozzles:
- Open also sometimes referred to as "standard" or "full-bore" having an inside diameter of ~22mm which is the standard soda bottle neck opening.
- Restricted which is anything smaller than the "standard". A popular restricted nozzle has an inside diameter of 9mm and is known as a "Gardena nozzle" named after a common garden hose quick connector used to make them.
The size of the nozzle affects the thrust produced by the rocket. Larger diameter nozzles provide faster acceleration with a shorter thrust phase, while smaller nozzles provide lower acceleration with a longer thrust phase.
It can be shown that the equation for the instantaneous thrust of a nozzle is simply:[5]
where 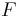 is the thrust,
is the thrust, 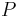 is the pressure and
is the pressure and 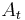 is area of the nozzle.
is area of the nozzle.
Fins
As the propellant level in the rocket goes down, it can be shown that the centre of mass initially moves downwards before finally moving upwards again as the propellant is depleted. This initial movement reduces stability and can cause water rockets to start tumbling end over end, greatly decreasing the maximum speed and thus the length of glide (time that the rocket is flying under its own momentum). To lower the centre of pressure and add stability, fins can be added which bring the centre of drag further back, well behind the centre of mass at all times, ensuring stability.
In the case of custom-made rockets, where the rocket nozzle is not perfectly positioned, the bent nozzle can cause the rocket to veer off the vertical axis. The rocket can be made to spin by angling the fins, which reduces off course veering.
Another simple and effective stabilizer is a straight cylindrical section from another plastic bottle. This section is placed behind the rocket nozzle with some wooden dowels or plastic tubing. The water exiting the nozzle will still be able to pass through the section, but the rocket will be stabilized.
Landing systems
Stabilizing fins cause the rocket to fly nose-first which will give significantly higher speed, but they will also cause it fall with a significantly higher velocity than it would if it tumbled to the ground, and this may damage the rocket or whoever or whatever it strikes upon landing.
Some water rockets have parachute or other recovery system to help prevent problems. However these systems can suffer from malfunctions. This is often taken into account when designing rockets. Rubber bumpers, Crumple zones, and safe launch practices can be utilized to minimize damage or injury caused by a falling rocket.
Another possible recovery system involves simply using the rocket's fins to slow its descent and is sometimes called backward sliding. By increasing fin size, more drag is generated. If the centre of mass is placed forward of the fins, the rocket will nose dive. In the case of super-roc or back-gliding rockets, the rocket is designed such that the relationship between centre of gravity and the centre of pressure of the empty rocket causes the fin-induced tendency of the rocket to tip nose down to be counteracted by the air resistance of the long body which would cause it to fall tail down, and resulting in the rocket falling sideways, slowly.
Launch tubes
Some water rocket launchers use launch tubes. A launch tube fits inside the nozzle of the rocket and extends upward toward the nose. The launch tube is anchored to the ground. As the rocket begins accelerating upward, the launch tube blocks the nozzle, and very little water is ejected until the rocket leaves the launch tube. This allows almost perfectly efficient conversion of the potential energy in the compressed air to kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy of the rocket and water. The high efficiency during the initial phase of the launch is important, because rocket engines are least efficient at low speeds. A launch tube therefore significantly increases the speed and height attained by the rocket. Launch tubes are most effective when used with long rockets, which can accommodate long launch tubes.
Safety
Water rockets employ considerable amounts of energy and can be dangerous if handled improperly or in cases of faulty construction or material failure. Certain safety procedures are observed by experienced water rocket enthusiasts:
- When a rocket is built, it is pressure tested. This is done by filling the rocket completely with water, and then pressurizing it to at least 50% higher than anticipated pressures. If the bottle ruptures, the amount of compressed air inside it (and thus the potential energy) will be very small, and the bottle will not explode.
- Using metal parts on the pressurized portion of the rocket is strongly discouraged because in the event of a rupture, they can become harmful projectiles. Metal parts can also short out power lines.
- While pressurizing and launching the rocket, bystanders are kept at a safe distance. Typically, mechanisms for releasing the rocket at a distance (with a piece of string, for example) are used. This ensures that if the rocket veers off in an unexpected direction, it is less likely to hit the operator or bystanders.
- Water rockets should only be launched in large open areas, away from structures or other people, in order to prevent damage to property and people.
- As water rockets are capable of breaking bones upon impact, they should never be fired at people, property, or animals.
- Safety goggles or a face shield are typically used.
- A typical two-litre soda bottle can generally reach the pressure of 100 psi (690 kPa) safely, but preparations must be made for the eventuality that the bottle unexpectedly ruptures.
- Glue used to put together parts of water rockets must be suitable to use on plastics, or else the glue will chemically "eat" away the bottle, which may then fail catastrophically and can harm bystanders when the rocket is launched.
Water rocket competitions
The Oscar Swigelhoffer Trophy is an Aquajet (Water Rocket) competition held at the Annual International Rocket Week[6] in Largs, Scotland and organized by STAAR Research[7] through John Bonsor. The competition goes back to the mid-1980s, organized by the Paisley Rocketeers who have been active in amateur rocketry since the 1930s. The trophy is named after the late founder of ASTRA,[8] Oscar Swiglehoffer, who was also a personal friend and student of Hermann Oberth, one of the founding fathers of rocketry.
The competition involves team distance flying of water rockets under an agreed pressure and angle of flight. Each team consists of six rockets, which are flown in two flights. The greater distance for each rocket over the two flights is recorded, and the final team distances are collated, with the winning team having the greatest distance. The winner in 2007 was ASTRA. The competition has been regularly dominated over the last 20 years by the Paisley Rocketeers.
The United Kingdom's largest water rocket competition is currently the National Physical Laboratory's annual Water Rocket Challenge.[9] The competition was first opened to the public in 2001 and is limited to around 60 teams. It has schools and open categories, and is attended by a variety of "works" and private teams, some travelling from abroad. The rules and goals of the competition vary from year to year.
The Water Rocket Achievement World Record Association.[10] A worldwide association which administrates competitions for altitude records involving single stage and multiple stage water rockets, a flight duration competition, and speed or distance competitions for water rocket–powered cars,
The oldest and most popular water rocket competition in Germany is the Freestyle-Physics Water Rocket Competition.[11] The competition is one part of a larger part of a student physics competition, where students are tasked to construct various machines and enter them in competitive contests.
Science Olympiad also has a Water Rocket event.
World record
The Guinness World Record of launching most water rockets simultaneously is in hands of Gotta Launch,[12] when on 19 June 2009, they launched 213 of them at the same time, together with students of the Delft University of Technology.
The current record for greatest altitude achieved by a water and air propelled rocket [13] is 2044 feet (623 metres), held by U.S. Water Rockets [14] on 14 June 2007. This altitude was calculated by averaging two flights. The first flight achieved 2068 feet (630 meters) and the second 2020 feet (615.7 meters). The rocket also carried a video camera as payload on both flights as part of the verification required by the competition rules.
Hot water rockets
A hot water rocket (or steam rocket) is a water rocket which uses hot blast water as its propellant. Water is kept in the rocket under pressure, at below its boiling point at that pressure. As it exits through a rocket nozzle, the pressure drops and the water instantly boils and expands against the nozzle and this greatly increases the exhaust speed and thrust.
The idea of such rockets was conceived by Germany before the Second World War, with the suggested use of an alternative rocket engine for launching fighter jets.
Bibliography
- D. Kagan, L. Buchholtz, L. Klein, Soda-bottle water rockets, The Physics Teacher 33, 150-157 (1995)
- C. J. Gommes, A more thorough analysis of water rockets: moist adiabats, transient flows, and inertials forces in a soda bottle, American Journal of Physics 78, 236 (2010).
References
- ^ Water Rocket Computer Model from NASA
- ^ Sim Water Rocket from Dean's Benchtop
- ^ Water Rocket Simulation from Clifford Heath's website
- ^ Dean's benchtop: hydrogen powered water rocket
- ^ Hydroflite: Rocket Science
- ^ Annual International Rocket Week
- ^ STAAR Research
- ^ ASTRA
- ^ National Physical Laboratory's annual Water Rocket Challenge
- ^ Water Rocket Achievement World Record Association
- ^ Freestyle-Physics Water Rocket Competition
- ^ Gottalaunch.com
- ^ Single stage water rocket altitude record competition rules
- ^ U.S. Water Rockets
External links
- WaterRocketLaunchers - How to build a rigid and highly efficient water rocket launcher out of very few common household components.
- The Water Rocket Achievement World Record Association – International association dedicated to the construction and safe operation of water rockets and the governing body for all water rocket world records.
- U.S. Water Rockets – Current altitude record holder – Aerial photography using water rockets
- Gotta Launch :: Water Rocket Insanity - World's most spectacular water rocket projects.
- Understand Water Rockets - A French water rocket website, includes videos, schematics to understand better Water Rockets
- Team Parental Advisory – Site that includes onboard and ground video. Also a WRA2 1000-foot Challenge competing team.
- International Rocket Week
- The Water Rocket Portal Free portal site hosting enthusiasts pages
- Water-rockets.com - Water-rocket science for hobbyist, students, and teachers of all ages.
- Water Rocket Annex
- Another Water Rocket Page
- Nick's Water Rockets
- Water rocket - A French water rocket website.
- Water rocket equations - The physics behind the rocket, including a simulator
- Backward sliding rockets
- Water rocket car - A water rocket car
- Aircommand water rockets - An Australian water rocket site with videos, tutorials, blogs and much more.
- Water Bottle Rocket - Water bottle rocket site with video and tutorials focusing on horizontal flight path, just like a RPG. Free Ebook to build your own RPG powered by water rocket.
- HHWRSA - Water Rocket Car website with videos, blog and howto's.